by Kristine Schmucker, HCHM Curator
When researching history, sometimes the only clues are a photograph. This is the case of a photograph of the George Kirk farm.

George Kirk Farm, ca. 1885, near Halstead, Ks. Lt-Rt ground: William, George Sr, Albert, Jane Kirk. Balcony Lt-Rt: Agnes, Maggie, James, Thomas, Jane, George Jr. Photo courtesy Jim Brower.
George & Jane Cooper Kirk: Harvey County Pioneers
The obituary for George Kirk of Halstead, Kansas noted:
“He at once distinguished himself as a pioneer of the kind that has made Kansas the leading commonwealth of the world.” (The Wichita Beacon, 12 December 1916, p. 3.)
So, who was this early Harvey County settler?
George Kirk born in Torrence of Campsie a suburb of Glasgow, Scotland 18 January 1840. He married Jane Cooper 21 October 1861. Their first child, William, was born in 1863 in Scotland.
George saw opportunities in the United States and in 1863 even “though the Civil War was raging, he set his face westward to bring his little family to the land where he thought there awaited them larger opportunities than were present in his native land.”
At first he worked as a coal miner and later, as a shaft foreman in the mines of northern Illinois. In the spring of 1871, the Kirk family moved to Kansas and took a homestead a mile and half north of the growing town of Halstead.
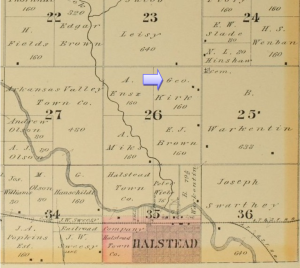
Halstead Township, Harvey County, Historical Atlas of Harvey County, Philadelphia: J.P. Edwards, 1882.
The Kirk family experienced tragedy in 1892. Nineteen year old, George, Jr, was living in Dighton, Ks, with his sister, Agnes and husband, William Curtis, when in a state of despair he “severed the Gordian know that bound him to this mundane state” and shot himself. In the letter he left to his parents he apologized for being “a very disobedient boy.” He noted that they had “suffered more on my account than any of the rest of the family” and urged his brothers “to obey their father and mother and they never will regret it all their days.” George had been living with his sister’s family for two months working with his brother in law on the railroad. Agnes, his sister, had not seen any signs “which would lead him to the rash act.” She had brought the gun back with her from Halstead a few days earlier.
George Sr died at home in Halstead, Kansas 7 December 1916. He was described as “hard working man of splendid integrity, faithful in every relation of life.” His wife, Jane Cooper Kirk, died 11 September 1917. They were survived by seven of their eight children.
L.A. Furlong, Halstead Photographer
Who was the photographer?
The photo was taken by L.A. Furlong, Halstead, Kansas. A census search revealed that John and Martha Furlong did live in Halstead at this time, but no connection could be found to L.A. Furlong.
A Google search revealed that there is at least one other photo attributed to “L.A. Furlong, Photographer, Halstead, Kansas.”
Other clues do not help much.
The 1867 St. Joseph, Missouri resident business directory lists L.A. Furlong. In addition, L.A. Furlong is mentioned as a “Gen’l Western Agent of the New Nork [sic]Central railroad . . . at Olis” in the Atchinson Daily Champion, 28 January 1876.
The photo of the Kirk family was taken around 1885 based on the possible ages of the Kirk children. The photo of “Chief Bull Thunder” is dated October 1885.
One other clue might be a brief news item in the Ottawa Daily Republic, 14 January 1888. A “well-dressed man, supposed from the papers on his person to be L.A. Furlong, of Illinois” was left by the train conductor in San Antonio, Tx. Reportedly, the man was “insane or bewildered from the effects of some drug” and he could not “talk coherently, and nothing can be learned from him.”
No other information could be found related to the man left at the train station or about L.A. Furlong, Halstead Photographer.
Sources: George Kirk Family
- The Wichita Beacon, 12 December 1916, 14 September 1917.
- Evening Kansan Republican 14 December 1916, 11 September 1917.
- Leavenworth Times 8 June 1892.
- Dighton Herald, 9 June 1892.
- Historical Atlas of Harvey County, Philadelphia: J.P. Edwards, 1882. HCHM Archives, Newton, Ks. See also the Kansas State Historical Society at http://www.kshs.org/p/county-atlases-or-plat-books/13859.
- Old Settler Official Program, 1917. HCHM Archives.
- U.S. Census 1880, 1900, 1910.
- Voter Registration, 1898, 1897. HCHM Archives.
- Harvey County Marriage Licenses, HCHM Archives.
Sources: L.A. Furlong, Halstead Photographer
- Ottawa Daily Republic, 14 January 1888, p. 1.
- Atchinson Daily Champion, 28 January 1876.
- St. Joseph, Missouri Residential and Business Directory, 1867. Jim Brower e-mail conversation with Susan K. Forbes, Historical Research Division, Kansas Historical Society, regarding the identity of L.A. Furlong.
- http://historical.ha.com/itm/photography/la-furlong-cabinet-photograph-of-chief-bull-thunder-medicine-man-bull-thunder-is-pictured-in-this-4-x-6-sepia-cabinet-c/a/679-72191.s
- Re: John & Martha Furlong Family. Evening Kansan, 25 February 1893, 18 May 1898, 26 May 1898, 31 December 1898, 9 January 1899,